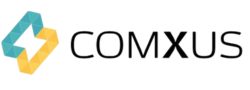The year 2025 is set to be a revolutionary year for businesses and industrial sectors. As the year begins, we can already see significant changes shaping the landscape of industrial networking.
These changes are driven by advancements in technology and evolving industry demands. Additionally, we are witnessing major improvements in efficiency and security.
To gain deeper insights, the Comxus Networking team conducted extensive research on industrial networks. Through this research, we identified 10 groundbreaking trends that will revolutionize industrial networking in 2025.

Rapid Progress of 5G and private 5G networks-
The deployment of 5G technology has been a game changer for industrial networking. 5G technology enables real-time communication with its low-latency capabilities. Also, 5G is a high-speed technology.
Due to which, Industries are increasingly adopting private 5G networks to enhance operational efficiency and control over their communications infrastructure.

Private 5G networks offer dedicated bandwidth. This will ensure reliable connectivity for critical applications such as robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and remote monitoring systems.
According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global industrial networking solutions market is segmented into various components. It includes solutions and services, with networking types divided into wireline and wireless, highlighting the growing importance of wireless solutions like 5G in industrial applications.
Key advantages of 5G technology –
- Ultra-low latency and high-speed connectivity for real-time operations.
- Dedicated bandwidth ensures secure and reliable communication.
- Supports automation with IoT, robotics, and AGVs in industrial environments.
Integration of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) –
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is growing as a central technology in industrial automation.
TSN boosts Ethernet networks by providing deterministic data transmission, which is crucial for applications requiring precise timing and synchronization such as motion control systems and real-time data analytics.
The adoption of TSN allows for the convergence of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) networks, simplifying architecture and reducing costs.
Key Advantage Of TSN –
- Enables deterministic data transmission for real-time industrial control.
- Reduces latency and packet loss in mission-critical applications.
- Simplifies IT-OT convergence for better network efficiency.
Expansion of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)-
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) continues to expand, connecting a multitude of devices and systems within industrial environments.
This connectivity facilitates data collection, analysis, and automation. Which may lead to improved decision-making and operational efficiency.

The global industrial networking solutions market is expected to grow significantly between 2024 and 2032, driven by the increasing adoption of IIoT devices and solutions.
Key Advantage Of IIOT –
- Enhances automation and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime.
- Provides real-time data analytics for better decision-making.
- Improves operational efficiency and supply chain management.
Implementation of Digital Twins –
Digital twin technology involves creating virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems.
These digital models allow industries to simulate, predict, and optimize performance in a virtual environment before applying changes in the real world.

The use of digital twins enhances decision-making, reduces maintenance costs, and improves product development cycles.
Comxus identifies digital twins as a significant trend in OT networking, emphasizing their role in predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
Key Advantage of Digital Twins –
- Enables real-time simulation for predictive maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Improves efficiency by testing changes before implementing them in physical assets.
- Enhances product development with data-driven insights.
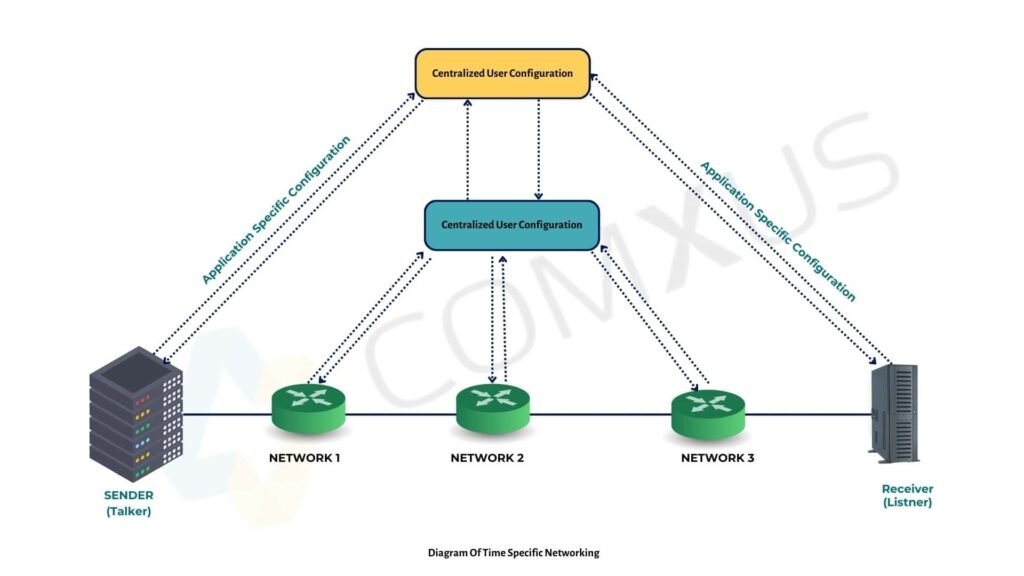
Implementation of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a cybersecurity approach that requires continuous verification of users and devices before granting access, ensuring strict control over who can connect to a network. Unlike traditional models that trust internal networks, ZTNA operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
In industrial networking, ZTNA helps to:
- Prevent unauthorized access by ensuring only verified entities connect.
- Reduce insider threats by limiting access to necessary permissions.
- Enhance remote security by securing access for remote workers.
- Minimize the attack surface by preventing lateral movement of threats.
ZTNA is especially useful in industries needing secure remote access, multi-layer authentication, and continuous security monitoring.
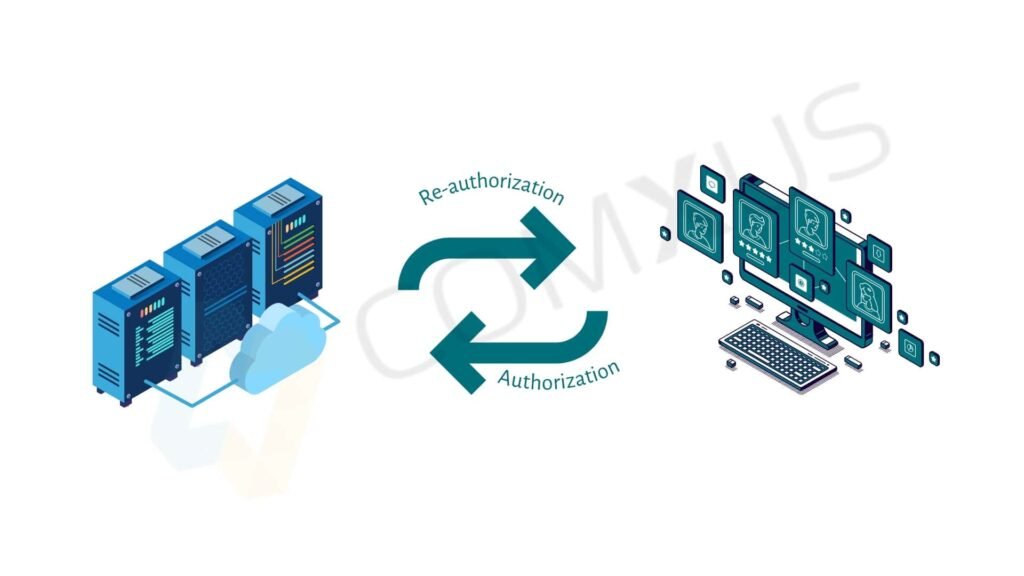
Adoption Of Network-as-a-Service (NaaS)
Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) is a cloud-based model that provides network services on-demand, allowing organizations to scale and manage their network infrastructure more flexibly and cost-effectively.
Instead of building and maintaining their own physical network, businesses can subscribe to NaaS, which offers services like bandwidth management, virtual networks, and security features.
The adoption of NaaS offers several benefits:
- Cost efficiency: Reduces the need for heavy capital investment in physical network hardware.
- Scalability: Easily adapts to the changing needs of businesses, allowing for quick adjustments in capacity.
- Simplified management: Cloud-based services are managed by the provider, reducing the complexity of network maintenance.
- Enhanced flexibility: Offers customizable solutions tailored to specific business requirements.
NaaS is gaining traction as more organizations look for flexible, scalable, and cost-effective networking solutions.
Adoption of Edge Computing
Edge computing is gaining traction as industries seek to process data closer to its source. By performing data analysis at the edge of the network, companies can achieve lower latency, reduced bandwidth usage, and enhanced security.
This approach is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time processing, such as quality control in manufacturing and predictive maintenance.
Key Advantage Of Edge Computing-
- Reduces latency by processing data closer to the source.
- Enhances security by minimizing data exposure to external networks.
- Lowers bandwidth costs by reducing cloud dependency.
As industries embrace digital transformation, staying ahead of these networking trends will be crucial for improving efficiency, security, and scalability. From 5G and TSN to AI-driven automation and cybersecurity, these innovations will shape the future of industrial networking in 2025 and beyond.